🏞️Most Ancient Religious Inscriptions
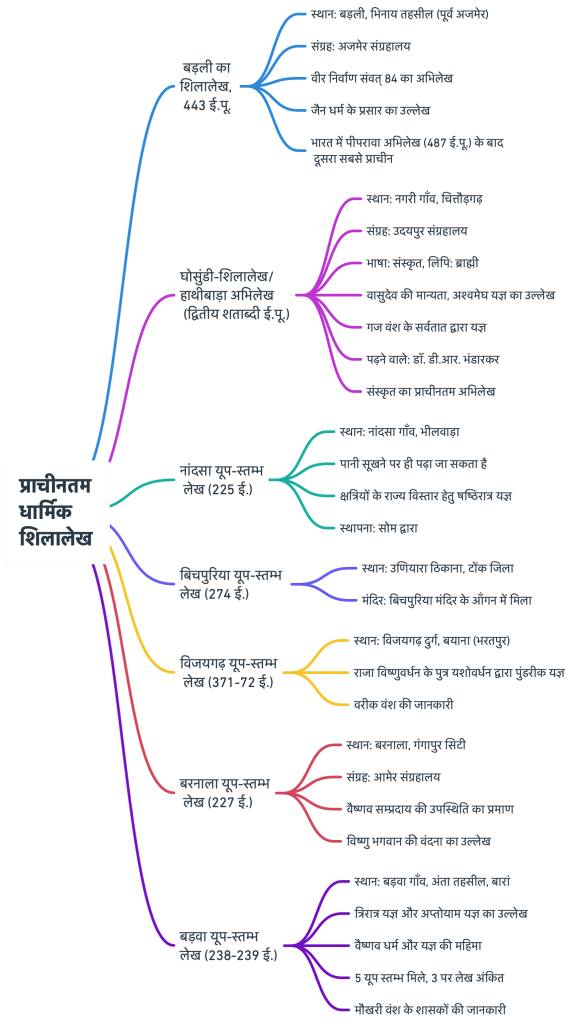
🏛️Ghosundi- Hathibada Inscription (2nd century BCE)
- 📍 Location: Nagari Village, Chittorgarh.
- 🏛️ Collection: Udaipur Museum.
- 📜 Key Information:
- 🖋️ Language: Sanskrit.
- ✍️ Script: Brāhmī.
- 🕉️ This inscription provides the earliest evidence of the Vaiṣṇava (Bhāgavata) sect in Rajasthan. Belief in Vāsudeva.
- 🔱 Mentions the Aśvamedha sacrifice performed by Sarvata of the Gaja dynasty.
- 📖 This inscription was first read by Dr. D.R. Bhandarkar.
- The most ancient inscription in Sanskrit
🌟Bāḍalī Inscription (443 BCE)
- 🏞️ Location: Bāḍalī, Bhīnāy Tehsil (former Ajmer) Kekaḍī District, obtained from the Bhīloṭ Mātā Temple.
- 📜 Key Information:
- 🕉️ Vīra Nirvāṇa Saṃvat (after the death of Mahāvīra) 84 year inscription.
- 📖 This is the oldest inscription in Rajasthan and the second oldest after the Piprahwa inscription (487 BCE) in India.
- 🌱 Mentions the spread of Jain religion.
- ✍️ This inscription is engraved in Brāhmī script.
- 🏛️ Collection: Preserved in the Ajmer Museum.
🏺Nāndsa Yūpa-Stambha Inscription (225 CE)
- 🌍 Location: Nāndsa Village, Sahāḍā Tehsil, Bhīlwāḍā.
- 💧 This inscription can only be read when the pond water dries up.
- 🕉️ Key Information:
- ⚔️ Guṇaguru performed the Ṣaṣṭhirātra sacrifice for the territorial expansion of the Kṣatriya kingdom.
- 📖 This inscription provides information about the prevalent Purāṇic sacrifices in northern India.
- 🏛️ Establishment: It is believed to have been established by Soma.
🏯Bīchpuriyā Yūpa-Stambha Inscription (274 CE)
- 🏞️ Location: Uṇiyārā Ṭhikānā, Ṭoṃk District.
- 🛕 Temple: Found in the courtyard of the Bīchpuriyā Temple.
🛡️Vijayagaḍh Yūpa-Stambha Inscription (371-72 CE)
- 🌄 Location: Vijayagaḍh Fort, Bayānā (Bharatpur).
- 🗡️ Key Information:
- 🔱 Yaśovardhana, the son of King Viṣṇuvardhana, performed the Puṇḍarīka sacrifice.
- 📜 The inscription provides information about the Vārīka dynasty.
✨Barnālā Yūpa-Stambha Inscription (227 CE)
- 📍 Location: Barnālā, Gaṃgāpur City.
- 🏛️ Collection: Preserved in the Āmer Museum.
- 🔔 Key Information:
- 🌸 Evidence of the presence of the Vaiṣṇava sect in ancient Rajasthan.
- 🙏 Mentions the veneration of Lord Viṣṇu at the end of the inscription.
🪔Baḍavā Yūpa-Stambha Inscription (238-239 CE)
- 🗺️ Location: Baḍavā Village, Aṃtā Tehsil, Bārāṃ.
- 📜 Key Information:
- 🔥 Mentions the Trirātra sacrifice and the Aptoyāma sacrifice.
- 🕊️ Reflects the glory of Vaiṣṇava religion and sacrifices.
- 🪵 5 Yūpa-Stambhas were found here, 3 of which have inscriptions.
- 📜 These inscriptions provide information about the rulers of the Maukharī dynasty.
- 🗓️ Mentions the Kṛta Saṃvat.

Other inscriptions:
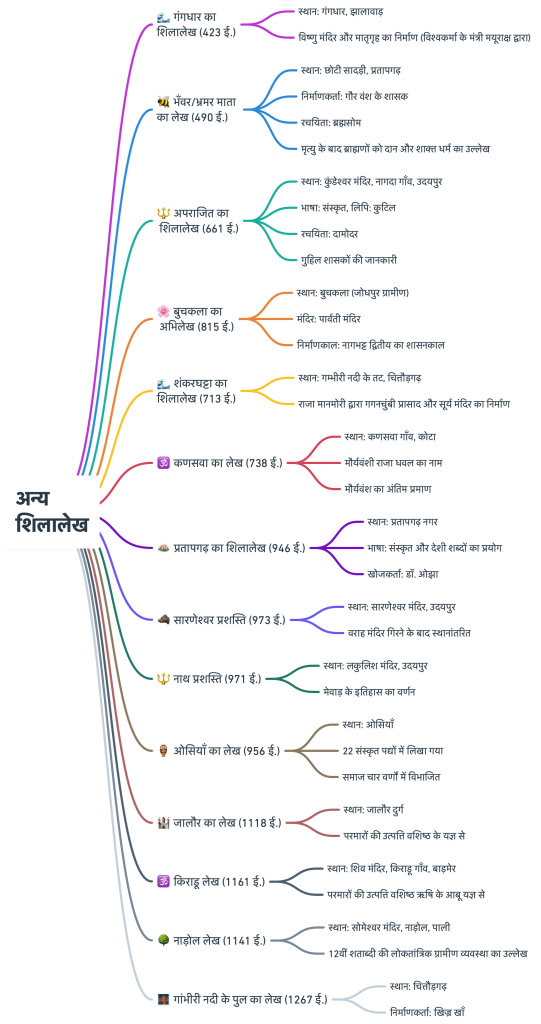
🌊Gangdhara Inscription (423 CE)
- 📍 Location: Gangdhara, Jhalawar.
- 🔧 Key Information:
- 🏛️ Mention of the construction of a Vishnu Temple by the minister Mayurāksha of Vishwakarma.
- 🌀 Mention of the construction of a Matrigriha in the Tantric style.
- 🏰 Sheds light on the feudal system of the 5th century.
🐝Bhavara/Bhramara Mata Inscription (490 CE)
- 📍 Location: Choti Sadri, Pratapgarh.
- 🏛️ Builder: Ruler of the Gaur Dynasty.
- 📜 Key Information:
- 🪔 Information about the Aulikara Dynasty.
- ✍️ Engraver: Purva.
- 🖋️ Author: Brahmasoma.
- 📜 Mention of donating to Brahmins after death and the Shakta religion.
🔱Aparajita Inscription (661 CE)
- 📍 Location: Kundeshwar Temple, Nagda Village, Udaipur.
- 📜 Key Information:
- ✍️ Author: Damodara.
- 🖋️ Language: Sanskrit.
- 📜 Script: Kutila.
- 📖 The inscription provides information about the Guhila rulers.
- 🏛️ It was read by Dr. Ojha and preserved at the Udaipur Victoria Hall Museum.
🌸Buchkala Inscription (815 CE)
- 🏛️ Location: Buchkala (Bilara – Rural Jodhpur)
- 🛕 Temple: Located in the assembly hall of the Parvati Temple
- ✍️ Construction Period: Reign of Nagabhatta II, son of King Vatsaraja Pratihara
- 🔎 Architect: Dei a son of Panchhariya
- 🪔 Discovered by: Brahmbhatt Nanuram
🌊Shankarghatta Inscription (713 CE)
- 📍 Location: Banks of the Gambhiri River, Chittorgarh.
- 📜 Key Information:
- 🏛️ King Manabhanga (Manmori) had a Gaganchumbhi Palace, Vapi, and a Sun Temple constructed.
- ✍️ Initial mention of worship of Shiva.
🪷Pratapgarh Inscription (946 CE)
- 🏛️ Location: Pratapgarh City, near the Chenaram Agarwal Baori
- ✨ Collection: Ajmer Museum
- ✍️ Language: Sanskrit and some vernacular words
- 🪔 Discovered by: Dr. Ojha
- 🌾 Meaning of vernacular words:
- 🏺Koshwah: Land irrigated with leather buckets
- 💐 Chausar: Garland of flowers
- 🛍️ Palika: Pula
- 🛢️ Pali: Measure of oil
- 🌾 Dhana: Dhani
- 🪔 Arhata
🕉️Kansawa Inscription (738 CE)
- 📍 Location: Kansawa Village, Kota.
- 📜 Key Information:
- 🏛️ Installed in a Shivalaya.
- ✍️ Name of Maurya Dynasty King Dhavala.
- 📖 The last evidence of the Maurya Dynasty in Rajasthan.
🐗Saranesvara (Sandanath) Prashasti (973 CE)
- 🏛️ Location: Previously located in the Varaha Temple of Ahad Village
- 🪷 Current Location: Saranesvara Temple, Udaipur
- 🏛️ After the Varaha Temple collapsed, it was installed in the Saranesvara Temple
🌄Nath Prashasti (971 CE)
- 🛕 Location: Lakulish Temple, Udaipur
- 🕊️ It describes the history of Mewar

🏺Osian Inscription (956 CE)
- 🛕 Location: Osian
- ✒️ Written in 22 Sanskrit verses
- 📜 Referred to Mansingh as the lord of the land and Vatsaraja as the subduer of enemies
- 🔎 Author: Padaja
- 🏛️ Society was divided into four varnas (Brahmin, Kshatriya, Vaishya, Shudra)
🕉️Kiradu Inscription (1161 CE)
- 🛕 Location: Shiva Temple, Kiradu Village (Barmer District)
- ✍️ Language: Sanskrit
- 📜 Key Information:
- 🪔 The origin of the Paramaras is said to be from the yagna of Sage Vasishtha at Mount Abu
🏰Jalore Inscription (1118 CE)
- 🏛️ Location: Jalore Fort (Toshkhana Building)
- ✨ Collection: Jodhpur Museum
- 📜 Key Information:
- 🔎 The origin of the Paramaras is said to be from the yagna of Sage Vasishtha
- 🛕 Vakpatiraj was the founder of the Jalore branch of the Paramaras
🌳Nadol Inscription (1141 CE)
- 🛕 Location: Someshwar Temple, Nadol (Desuri Tehsil, Pali)
- 📜 Key Information:
- 🌾 Mentions the democratic rural system of the 12th century
- 🐎 Bhats carried goods on horses and engaged in horse trade
- 🐂 Banjaras transported goods on bullocks and engaged in barter trade
🌉Inscription on the Bridge of Gambhiri River (1267 CE)
- 🛕 Location: On the ninth arch of the bridge over the Gambhiri River in Chittorgarh District
- 🏗️ Builder: Khizr Khan
Inscriptions related to Mewar
🌟Inscription of Manmori (713 CE)
- 📍 Location: Putholi village, Chittorgarh.
- 📜 Key Information:
- 🏞️ Site: Located on the banks of Lake Mansarovar.
- ✍️ Author: Nagabhatta, son of Pushya.
- 📖 Engraved by: Karuna, son of Shivadity.
- 📝 Colonel James Tod read this inscription.
- 🌊 This inscription was thrown into the sea due to its heavy weight.
- 📖 Tod published it in his work ‘Annals and Antiquities of Rajasthan’.
- ✨ The text mentions Amrita Manthana.
- 🕉️ Evidence of the Mauryas’ connection to Rajasthan
🏛️Inscription of Chirwa (1273 CE)
- 🛕 Location: Temple in Chirwa village, Badgaon tehsil, Udaipur district
- 📜 Language: Sanskrit
- ✒️ Script: Devanagari
- 📜 Key Information:
- 🏰 Mention of the Guhilot rulers of Mewar (Jaitrasimha, Tejasimha, Samarsimha)
- ✍️ Composed by: Ratnaprabhu Suri, disciple of Bhuvanasimha Suri
- ✒️ Engraved by: Their disciple Parshvachandra
- Dilhan had it installed on the wall
- 🌟 Mention of Chetagachcha Acharyas
- 📜 Sati practice, grazing land and Pashupath Shaivism
- 📜 Administrative post of Talaraksha
Inscription of Chittorgarh (971 CE)
- 🛕 Location: Chittorgarh
- 🖋️ Copy preserved in the Indian Temple in Ahmedabad
- ✍️ Construction of the Mahavira Jinalaya by the ruler of Chittorgarh, Narvarma
- 🔒 Women’s entry was prohibited in the temple, reflecting the social system of that time
🛕Ranakpur Prashasti (1439 CE)
- 📍 Location: Chaumukha Jain Temple in Ranakpur, Desuri tehsil, Pali district
- 📜 Language: Sanskrit
- ✒️ Script: Devanagari
- 🛠️ Sculptor: Depak
- 📖 Key Information:
- 🏰 Mention of the achievements of the rulers of Mewar from Bappa to Kumbha
- 🏛️ Introduction of the Dharanaka Shah Shreshti lineage
- 🏰 Bappa and Kalbhoj are described as distinct personalities
- 💰 Evidence of the currency called “Nanaka”
🌄Nath Prashasti (971 CE)
- 🛕 Location: Lakulish Temple, Udaipur
- 🖋️ Language: Sanskrit
- 📖 Script: Devanagari
- 🕊️ It describes the history of Mewar
🌳Inscription of Rasiya’s Chhatri (1274 CE)
- 🛕 Location: Behind the Rajmahal in Chittorgarh district
- 📜 Key Information:
- 🏰 Mention of the Guhilot rulers (from Bappa to Narvarma) of Mewar
- ✍️ Author: Ved Sharma, son of Priyapatu
- 🌟 Description of 13th century life and natural conditions
- 🛕 Mentioned locations: Nagda and Delwara
📜Kheroda Copper Plate (1483 CE)
- 📖 Key Information:
- 💰 Information about the currency in use during the time of Maharana Kumbha



